Introduction: Anxiety is a basic emotion that has existed since humans evolved. It’s found in many people and is also present in various anxiety disorders, making it important for doctors to understand. We’ve learned a lot about anxiety disorders recently through studying how they’re classified, how common they are, and how they affect people. Treatment options like medication and therapy have improved, giving hope to those struggling with anxiety. This article aims to provide an overview of recent advancements in understanding the use of medicinal cannabis for anxiety treatment and the current trends in prescribing practices.
Anxiety Disorders: Anxiety comes from the Latin word “anxietas,” meaning to choke, trouble, or upset. It includes how we behave, feel, and think when we feel in danger. Feeling a bit anxious can be normal and even helpful in some situations. But when anxiety becomes too much or lasts too long, it can cause problems in daily life. Anxiety disorders happen when this anxiety becomes excessive or doesn’t fit the situation, causing distress and affecting how we function in different areas of life.
Classification of Anxiety Disorders: Anxiety disorders are grouped into different categories based on how they affect people. The DSM-IV lists various types, including panic disorder, social phobia, generalized anxiety disorder, and others. It also includes anxiety related to other conditions like substance abuse.
Why This Review of Anxiety Disorder Research in India: Anxiety disorders are closely linked to stress and how we cope with it, which is influenced by our culture. Culture affects how we show symptoms, explain illness, and seek help. This review aims to look at how cultural differences impact anxiety disorders in India and highlight areas where more research is needed.
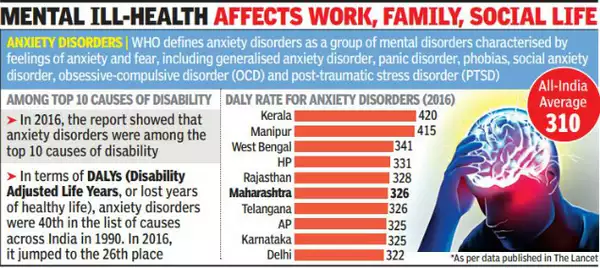
Epidemiological Studies: There have been several studies in India looking at how common anxiety disorders are. They found that anxiety disorders are more common in cities than in rural areas. They are also more common in women. However, there’s still a need for more research, especially in rural areas, to understand these disorders better.
Epidemiology of Anxiety Disorders in the Elderly: There’s not much research on anxiety disorders in elderly populations in India. One study found that about 9% of elderly people in a rural area had anxiety disorders, but there may be biases in the data.
Epidemiology of Anxiety Disorders in Children: Studies on anxiety disorders in children in India exist. However, they often do not separate anxiety disorders from other mental health problems. One study found that about 9.7% of children seen in outpatient clinics had anxiety disorders, with girls being more affected than boys.
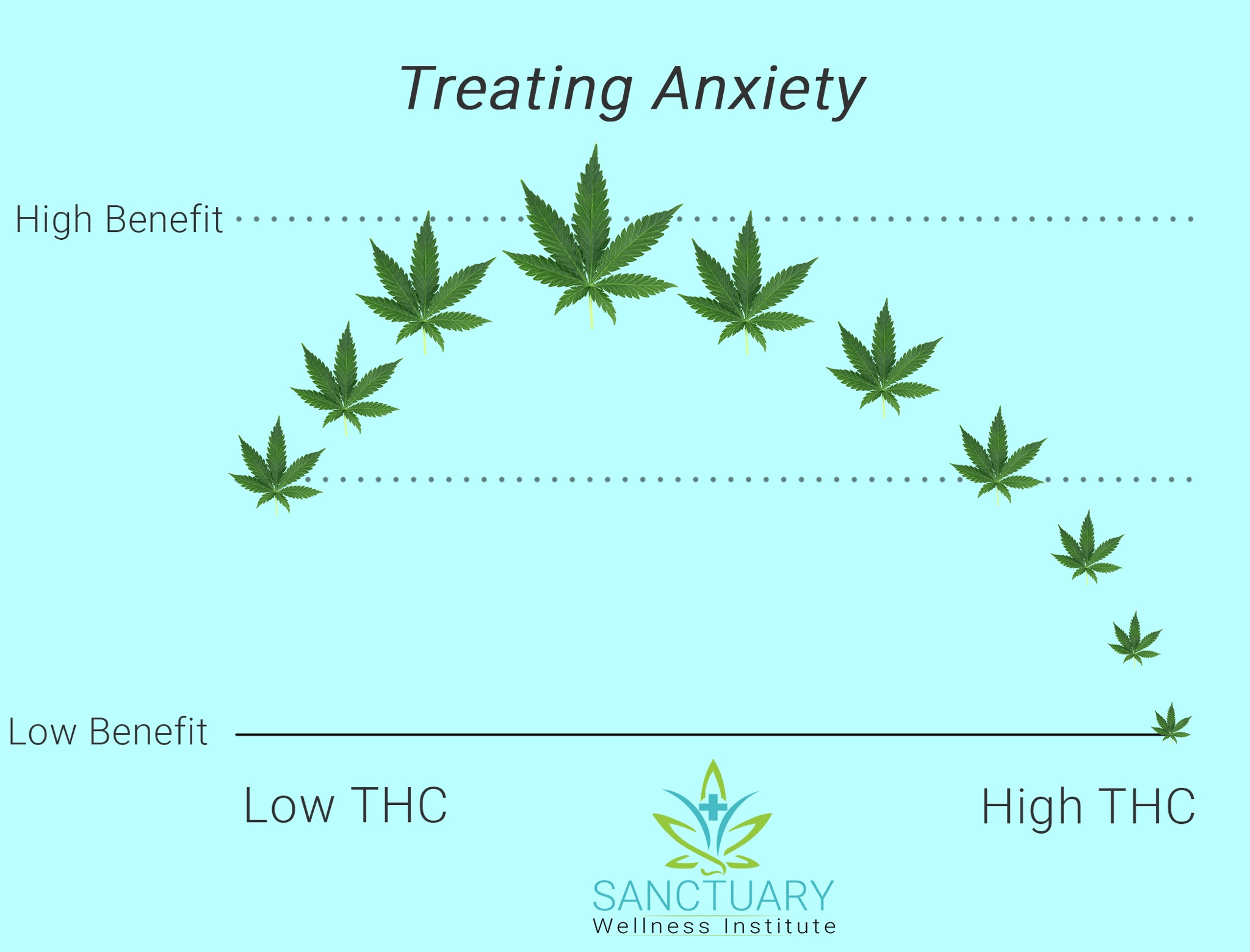
Photo courtesy : Sanctuary wellness institute,
Discussion: Studies, both clinical trials and laboratory experiments, indicate that CBD may have anxiety-relieving effects in both healthy individuals and those with anxiety disorders. However, there isn’t enough evidence to consider CBD as the first choice for treatment. The effectiveness of THC-dominant products in treating anxiety remains uncertain, with some individuals experiencing worsened anxiety while others find relief. It’s important to note that THC can impair cognitive function and driving ability. Despite the lack of robust evidence, the prescription of medicinal cannabis for anxiety is increasing, alongside the widespread use of illicit cannabis for self-medication. Approximately 17% of current prescriptions for anxiety involve CBD-dominant products, while the majority consist of THC-containing products and herbal cannabis. Healthcare providers should weigh the potential risks and benefits before prescribing medicinal cannabis for anxiety and adopt a cautious approach.
Recent years have seen growing interest in the therapeutic potential of medicinal cannabis products. Anxiety disorders rank as the second most common reason for prescribing these products in Australia, following chronic pain.
Given the increasing use of cannabis and medicinal cannabis for anxiety, it’s crucial to examine the rationale behind their use and the current evidence regarding their efficacy and safety.
The Endocannabinoid System: The potential for using medicinal cannabis in anxiety treatment stems from its interaction with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a biological system that regulates various physiological processes, including mood, sleep, and cognition. Preclinical studies suggest that cannabinoids can modulate fear and anxiety by acting on ECS receptors in the brain.
Phytocannabinoids: Cannabinoids derived from plants, particularly THC and CBD, are the focus of therapeutic research. THC acts on ECS receptors and can cause intoxicating effects, while CBD does not produce intoxication and has been associated with reducing anxiety in both animal models and clinical trials.
Efficacy of Medicinal Cannabis for Anxiety: Numerous medicinal cannabis products are available, with varying THC and CBD content. Clinical trials investigating cannabinoids for anxiety have yielded mixed results. While THC may offer marginal benefits, particularly in alleviating pain, CBD shows promise in reducing anxiety severity. However, larger trials are needed to confirm its efficacy, especially at lower doses.
Safety, Adverse Effects, and Drug Interactions: THC can induce side effects such as nausea, dizziness, and euphoria, and may exacerbate anxiety in some individuals. CBD, on the other hand, is generally well-tolerated, although it can interact with certain medications, necessitating cautious dosing and monitoring.
Prescribing Uncertainties: Prescriptions for medicinal cannabis for anxiety are increasing rapidly, but there is limited guidance on appropriate dosing and combination with other medications. Additionally, the affordability of high CBD doses remains a concern, and the down-scheduling of low-dose CBD products may further complicate prescribing practices.
Conclusion: Anxiety disorders represent a significant portion of prescriptions for medicinal cannabis, despite limited evidence supporting its efficacy, particularly for THC-dominant products. CBD shows promise in reducing anxiety severity, but further research is needed to establish optimal dosing and safety profiles. Prescribers should carefully weigh the risks and benefits of medicinal cannabis for anxiety and remain vigilant for potential drug interactions and adverse effects.
References :
https://journals.lww.com/indianjpsychiatry/fulltext/2010/52001/an_overview_of_indian_research_in_anxiety.32.aspx#
https://www1.racgp.org.au/ajgp/2022/august/medicinal-cannabis
cover photo: courtesy times of India


Excellent observation as far as Cannabis & Opium Considered especially in Bharath, from Vedic periods onwards connected with our Cultural ceremony so it should be liberalized instead of treating as a banned Drug