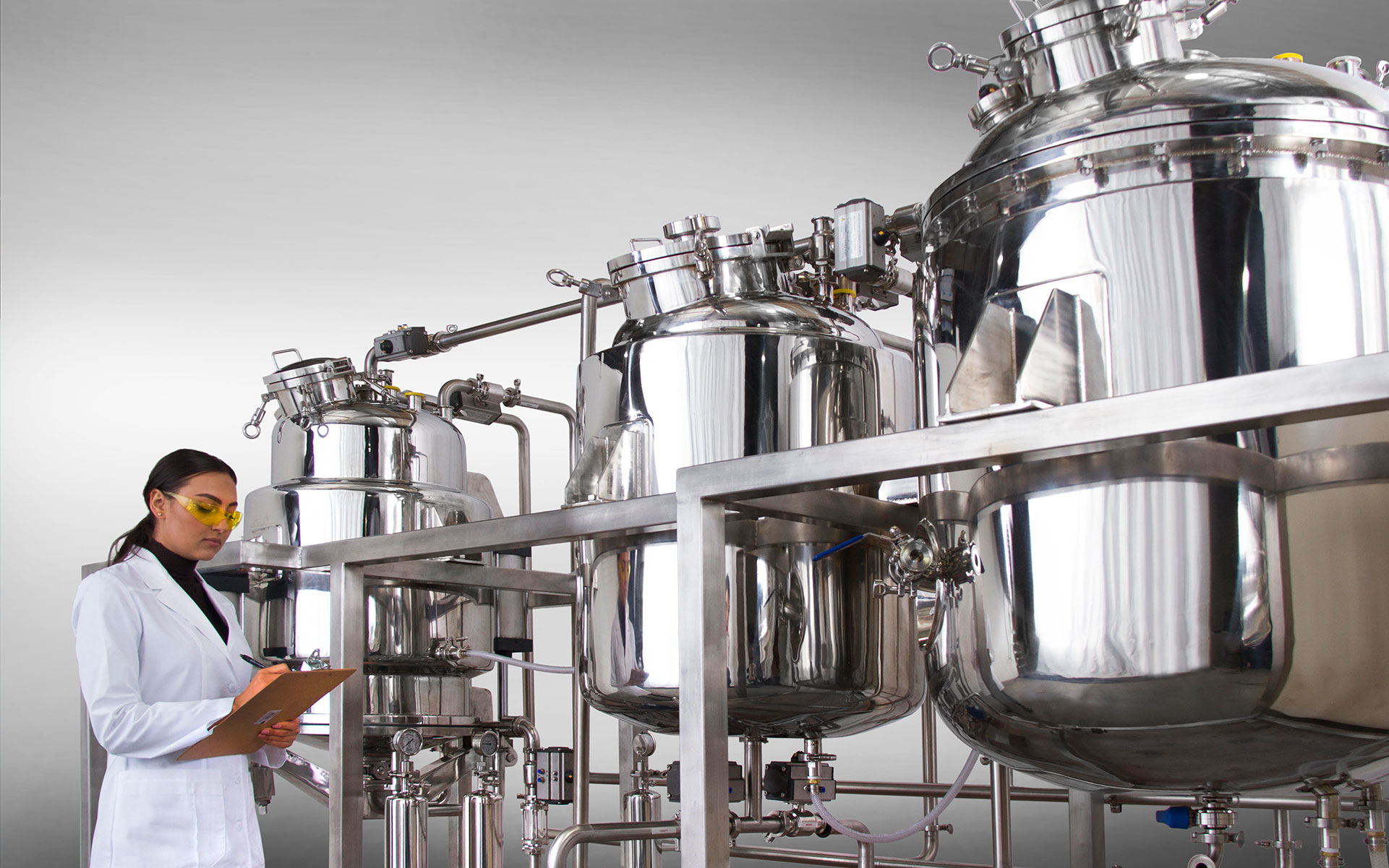
Cannabinoid extraction methods are techniques used to isolate and extract the active compounds, known as cannabinoids, from the cannabis plant. These methods are employed to obtain cannabinoids such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) for various purposes, including medical, scientific, and recreational applications. Here are some commonly used cannabinoid extraction methods:
1.Solvent Extraction:
Ethanol Extraction: This method involves soaking the plant material in ethanol (high-proof alcohol) to extract cannabinoids. The ethanol dissolves the cannabinoids, and the resulting solution is then evaporated to remove the solvent, leaving behind the cannabinoids.
Hydrocarbon Extraction: It uses hydrocarbons such as butane or propane to extract cannabinoids. The plant material is soaked in the hydrocarbon solvent, which dissolves the cannabinoids. The solution is then purged of the solvent, typically through evaporation or vacuum processes.
2. CO2 Extraction:
Supercritical CO2 Extraction: This method utilizes carbon dioxide (CO2) in a supercritical state, where it exhibits properties of both a liquid and a gas. CO2 is used as a solvent to extract cannabinoids at specific temperatures and pressures. The resulting extract contains the desired cannabinoids, and the CO2 is then separated and recycled for reuse.
3. Rosin Press Extraction:
This technique involves applying heat and pressure to the cannabis plant material, typically using a specialized device called a rosin press. The heat and pressure cause the cannabinoids to be squeezed out of the plant material, resulting in a sticky resinous substance called rosin.
4. Solventless Extraction:
Ice Water Hash or Bubble Hash: This method uses ice-cold water and agitation to separate trichomes (resin glands containing cannabinoids) from the plant material. The mixture is filtered through screens of varying micron sizes to collect the trichomes, which are then dried and pressed into hash.
There are few more general methods
a) Olive Oil Extraction:
This is a simple and safe method that involves using olive oil as a solvent to extract cannabinoids. The plant material is decarboxylated (heated) to activate the cannabinoids, and then it is mixed with olive oil and heated for a certain period of time. The cannabinoids dissolve into the oil, resulting in an infused oil that can be used in various applications.
b) Solvent-Assisted Vacuum Extraction (SAVE):
SAVE is a technique that combines solvent extraction with vacuum distillation. It involves using a vacuum to lower the boiling point of the solvent, allowing for lower-temperature extraction. The solvent is heated and circulated through the plant material, extracting the cannabinoids. The vacuum then helps evaporate the solvent more efficiently.
c) Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE):
This method utilizes microwave energy to accelerate the extraction process. The plant material is mixed with a solvent, such as ethanol, and then subjected to microwave irradiation. The microwaves generate heat, promoting the extraction of cannabinoids from the plant material into the solvent. MAE can reduce extraction times compared to traditional methods.
d) Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE):
PLE, also known as accelerated solvent extraction (ASE), employs elevated temperatures and pressures to extract cannabinoids. The plant material is loaded into an extraction cell, and a solvent, such as ethanol or a mixture of solvents, is pumped through the cell at high pressure and temperature. The cannabinoids are dissolved in the solvent, and then the extract is collected.
e) Ultrasonic Extraction:
Ultrasonic extraction involves using high-frequency sound waves to disrupt the plant material and facilitate the extraction of cannabinoids. The plant material is mixed with a solvent and subjected to ultrasonic waves, which create cavitation bubbles that implode, releasing energy and causing the cell walls to rupture. This enhances the extraction process and increases the yield of cannabinoids.
It’s important to note that different extraction methods can have varying efficiencies, costs, and safety considerations. The choice of method often depends on factors such as the desired end product, scale of production, equipment availability, and regulatory requirements.