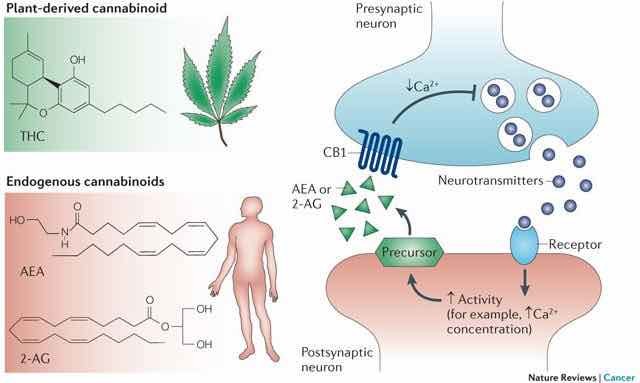
Cannabis and anandamide have a close relationship and can both have effects on the human body and mind. Anandamide, often referred to as the “bliss molecule,” is an endocannabinoid naturally produced in the body. It is structurally similar to the cannabinoids found in cannabis plants. When it comes to the effects of cannabis and anandamide, there are several key points to consider:
- Cannabinoid receptors: Both cannabis and anandamide interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in the body. The ECS is a complex network of receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids that helps regulate various physiological processes such as mood, pain, appetite, and sleep.
- Psychoactive effects: Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, particularly the CB1 receptors, producing the well-known euphoric and intoxicating effects. Anandamide, although less potent than THC, also binds to CB1 receptors and can contribute to mood enhancement and a sense of well-being.

- Similar effects: Both cannabis and anandamide can produce similar effects such as relaxation, mild euphoria, pain relief, and appetite stimulation. This is because they activate the same cannabinoid receptors in the brain and body.
- Duration of effects: The effects of cannabis are typically more pronounced and longer-lasting compared to anandamide. Anandamide is rapidly broken down by enzymes called fatty acid amide hydrolases (FAAH), whereas THC in cannabis can persist in the body for several hours.
- Regulation of anandamide: It is believed that cannabis use can influence the production and regulation of anandamide in the body. Some research suggests that chronic cannabis use may lead to downregulation of cannabinoid receptors, reducing the body’s natural production of anandamide and potentially affecting the endocannabinoid system’s overall functioning.
It is important to note that the effects of cannabis can vary greatly depending on the specific strain, cannabinoid profile, individual tolerance, and mode of consumption. Additionally, while cannabis has therapeutic potential for various medical conditions, it can also have potential side effects and risks, particularly when used excessively or by individuals with certain vulnerabilities or predispositions. It’s always advisable to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and information.